Learn from the AEMUS Experts
Building ultrasound knowledge doesn’t start and end with your exam: What you use to learn—and who you learn from—will serve you for the rest of your career.
With the new Advanced Ultrasound Qbank, you can pass your FPD exam and provide better care with practice questions written by the experts.
Join these experts in
closing knowledge gaps for your exam and the future of ultrasound.
The
Ultrasound
Qbank
Created by point-of-care ultrasound champions.
Real Ultrasounds.
Real Results.
Test your knowledge with practice questions including real ultrasound cases and scenarios.
Ready to close your knowledge gaps?
Get 30-day, 90-day, or 365-day access to the Advanced Ultrasound Qbank
Inside Your Qbank
Practice questions based on the AEMUS core content blueprint—pass guaranteed.
Blueprint
-
CategoriesDistribution
-
Physics and Technical Aspects of Ultrasonography10 ± 5%
-
Anatomic / Diagnosic Ultrasound60 ± 5%
-
Procedural Ultrasound10 ± 5%
-
Education and Research Skills10 ± 5%
-
Administration and Quality10 ± 5%

Question
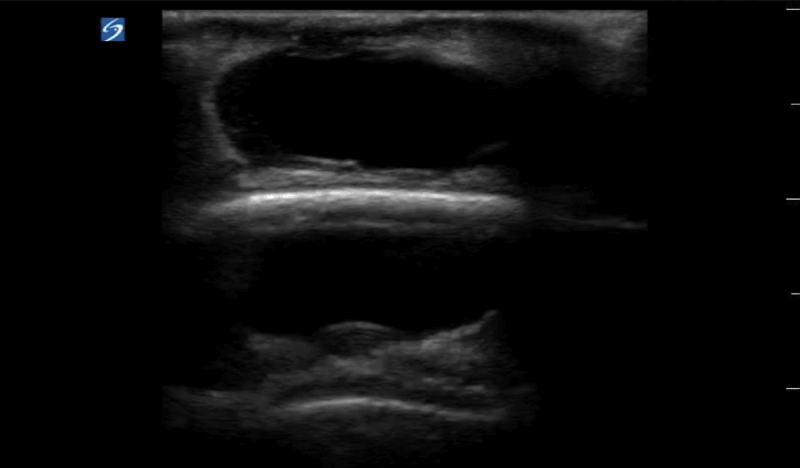
A 60-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a painful lump to the back of his head. He was hit in the head with a baseball bat 2 weeks prior and recently got his sutures removed. On physical exam he has a tender and fluctuant mass. The skin exam is limited because of his hair. A point-of-care ultrasound is performed as shown above. What is the next best step?
Explanation
Soft tissue ultrasound is performed using a high-frequency linear transducer. In this grayscale image, the mass appears as an anechoic rounded structure, making it indistinct from a cyst, seroma, hematoma, abscess, or vascular anomaly. The mass is also on top of the scalp and the hyperechoic stripe of the scalp creates a mirror artifact. Performing color Doppler on any mass will identify if there is a source of blood flow within the cavity. Color Doppler can also help delineate a lymph node from other pathology. The image above is a pseudoaneurysm that formed after trauma. Pseudoaneurysms occur due to extravasation of blood outside of the vessel wall and into the perivascular space.
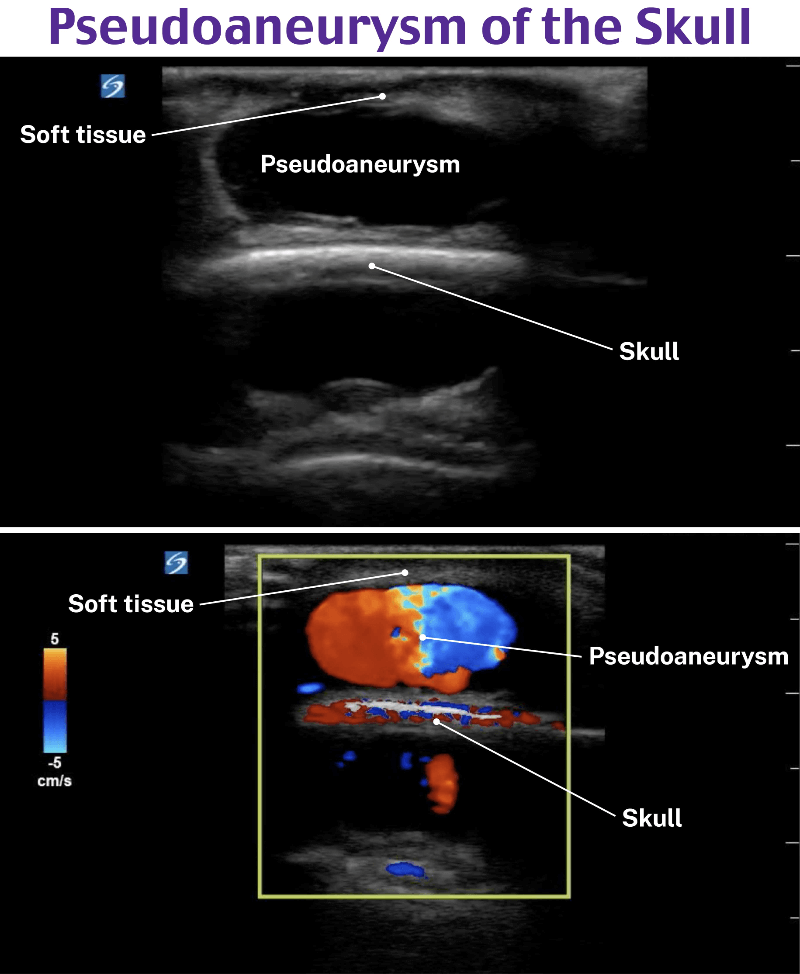
Antibiotics and follow-up (A) as well as incision and drainage (C) are incorrect answers because this is a pseudoaneurysm. An abscess is also an anechoic or hypoechoic fluid collection within a rounded cavity and often has irregular borders. Without using color Doppler, it can be indistinguishable from other fluid-filled masses. Needle aspiration (B) is also an incorrect answer because puncturing the pseudoaneurysm may cause more complications including external hemorrhage. There are a few ways to treat a pseudoaneurysm. First compress the mass using a linear transducer for approximately 20 minutes until pseudoaneurysm communication is closed. Another treatment option is injecting thrombin into the pseudoaneurysm. If the first two treatments fail then the pseudoaneurysm may require surgical intervention.
Overall Performance
- Focused H&P 70%
- Diagnosis 80%
- Consultation 75%
- Prognosis 82%














