Podcast Ep 28: Vaginal Bleeding, DSM-V, & More

Welcome back to Episode 28! We are already well into intern year. Remember it is a roller coaster, with ups and downs, but in the end, you will really appreciate just how far you have come. This week we start off with a quick ophthalmology review and then dive into the new material, covering OB/GYN, pediatric dermatology, torsades de pointes, and much more. Let’s get started.

- Acute angle closure glaucoma classically presents with painful monocular vision loss. The pupil would be fixed and mid-dilated with a hazy cornea and perilimbic injection.
- Optic neuritis is characterized by central vision loss with preserved peripheral vision. Patents may also have pain with eye movement and reduced color vision.
- Retinal detachment is associated with painless monocular vision loss with floaters and flashing lights. The retina can appear dull and gray. Call ophthalmology immediately for any retinal detachment.
Now onto this week’s podcast.
Question 1
A 27-year-old woman presents with vaginal bleeding. Her last menstrual period was eight weeks ago. On physical examination, there is a small amount of blood in the vaginal vault with an open internal cervical os. Bedside ultrasound reveals an intrauterine pregnancy with a fetal pole but no heartbeat. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Incomplete miscarriage
B. Inevitable miscarriage
C. Missed abortion
D. Threatened miscarriage
Question 2
How does the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-V) code personality and developmental disorders?
A. Axis I
B. Axis II
C. Section I
D. Section II
Question 3
A 35-year-old woman with a known history of seizure disorder is actively seizing in the ED. Which of the following is the first-line medication and route to treat her seizure?
A. Intramuscular fosphenytoin
B. Intravenous midazolam
C. Oral lorazepam
D. Rectal diazepam
Question 4
Which of the following statements is true regarding airway management in children?
A. Adults are more susceptible to airway obstruction than children
B. Children have a lower basal oxygen consumption compared to adults which results in relative protection from hypoxia and decreased need for pre-oxygenation
C. The glottic opening in children is more anterior compared to that of adults
D. The vocal cords are the narrowest portion of the airway in children compared to the cricoid ring in adults
Question 5
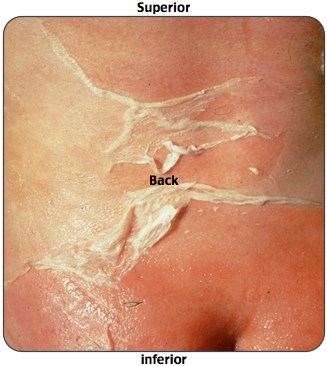
An 11-month old male is brought in by his mother for fever, irritability, and rash. She reports that other children at his daycare have similar symptoms. You see the following on physical exam as seen above. Which of the following is true regarding this condition?
A. Intravenous steroid administration is the mainstay of therapy
B. It is less common in children over 6 years of age
C. Nikolsky’s sign is negative
D. The condition is uniformly fatal
Question 6
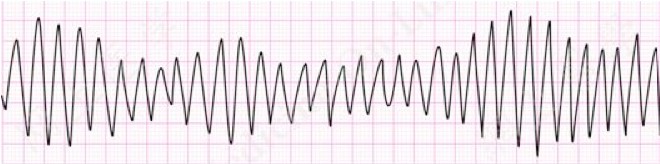
A patient with palpitations presents to the ED. Her rhythm strip is seen above. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management?
A. Amiodarone
B. Cardioversion
C. Magnesium sulfate
D. Transvenous pacing at 60-80 bpm

- An incomplete abortion occurs before 20 weeks when the os is open and POC are visible either in the OS or in the vaginal canal.
- An inevitable miscarriage presents with an open os without passage of any products of conception.
- A missed abortion is a broader term that describes several conditions, in which the fetus is no longer viable, but remains intrauterine with a closed OS.
- A threatened abortion is defined as any vaginal bleeding during pregnancy with a confirmed intrauterine pregnancy and a closed OS.
- DSM-V is organized by sections. The multiaxial system of DSM-IV is gone. In DSM-V, Section 2 covers diagnostic categories and Section 3 covers conditions that need additional research.
- In an actively seizing patient the first priority is airway protection – roll the patient onto the left lateral decubitus position to prevent aspiration.
- The first line pharmacologic management for a patient in status epilepticus is a parenteral benzodiazepine. Midazolam has the fastest onset.
- Second line agents for status epilepticus includes phenytoin, fosphenytoin, valproic acid, phenobarbital, or levetiracetam.
- Do not forget to check a finger stick and consider INH toxicity in those in status epilepticus.
- The glottic opening in children is more anterior to that of adults.
- The narrowest portion of the pediatric airway is the cricoid cartilage.
- As compared to the adult airway, in the pediatric airway, the tongue is proportionally larger and the epiglottis is longer and narrower.
- Staph scalded skin syndrome most commonly affects those under 2 years of age, and it rarely occurs in those over 6 years of age.
- Staph scalded skin syndrome is treated with IV fluids, aggressive wound management, and an anti-staphylococcal antibiotic.
- Torsades de pointes is associated with a prolonged QT interval, hypomagnesemia, and hypokalemia.
- Torsades de pointes is treated with intravenous magnesium.
That wraps up Episode 28. From psychiatry to obstetric emergencies to pediatric dermatology, we have covered the entire spectrum of emergency medicine this week. Hope you all enjoyed. Do not forget to listen for the trauma phone ring tone in the coming weeks for a chance to win a Rosh Review Subscription. Remember to tweet us @Roshcast or email us at Roshcast@roshreview.com the exact time you hear the ring to win the prize.
Until next time,
Jeff and Nachi
Get Free Access and Join Thousands of Happy Learners
You must be logged in to post a comment.





Comments (0)