Rapid Review: Epiglottitis

Reviewed January 2024
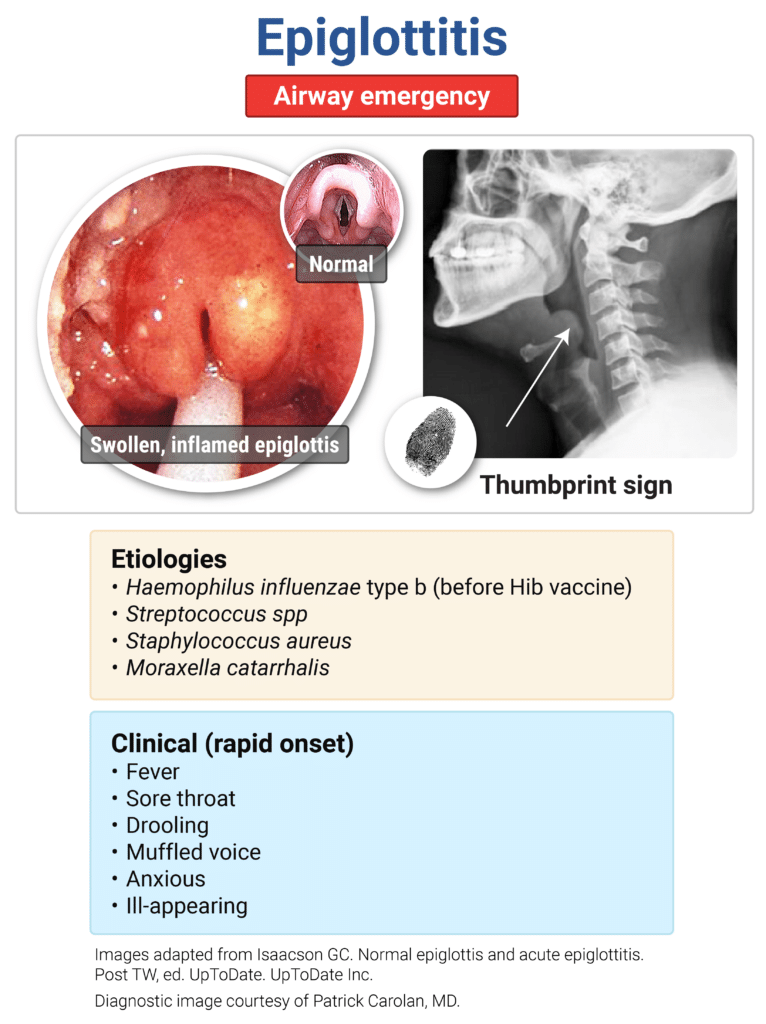
Epiglottitis
- Sx: rapid onset of fever, muffled voice, dysphagia, respiratory distress
- PE: sore throat, stridor, leaning forward, drooling, red swollen epiglottis on direct visualization
- Imaging: enlarged epiglottis (thumbprint sign) on lateral neck X-ray
- Most commonly caused by H. influenzae (decrease since Hib vaccine), Strep and Staph species
- Treatment is airway management and IV antibiotics (third-generation cephalosporin AND antistaphylococcal)
Sample question:
A 5-year-old boy presents to the emergency department because of difficulty breathing that began a few hours prior to consult. The caretaker reports that he was apparently well until he developed a fever and sore throat yesterday. He has no cough. On examination he is noted to be flushed, maintaining a sitting position with his neck hyperextended and arms braced forward. He is also febrile and has low-pitched inspiratory stridor. Which of the following was the most common etiologic agent responsible for the boy’s disease in the pre-vaccination era?
Get Free Access and Join Thousands of Happy Learners
You must be logged in to post a comment.





Comments (0)