Rapid Review: Hypercalcemia

Reviewed February 2024
Hypercalcemia
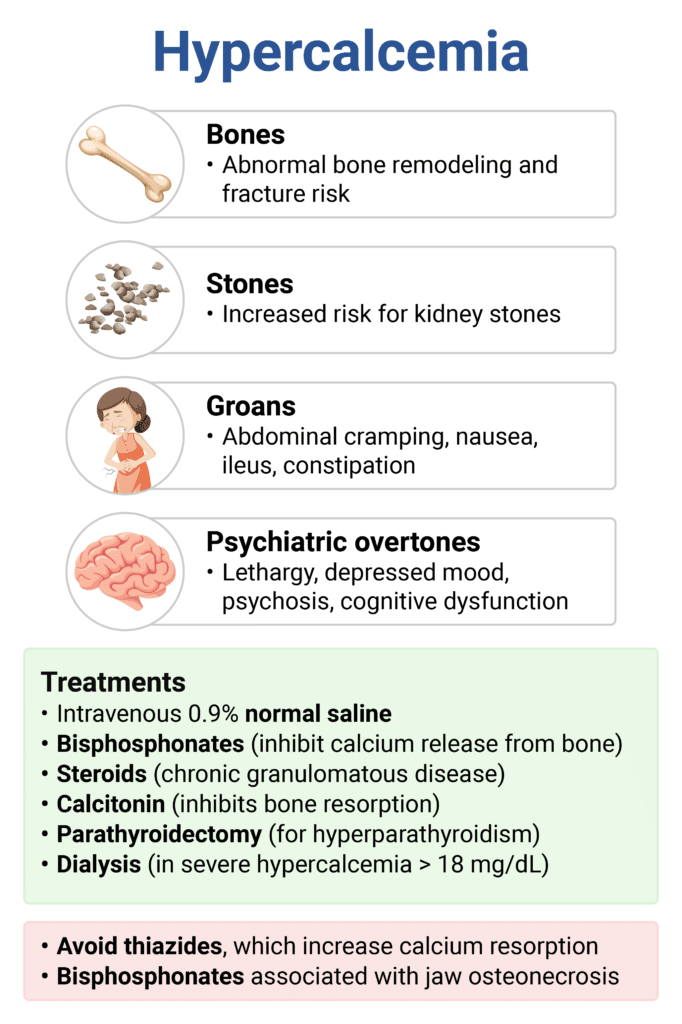
- Sx: bone pain (bones), kidney stones (stones), abdominal pain (groans), lethargy, psychosis (psychiatric overtones)
- ECG: shortened QT interval
- Most common causes
- Malignancy (most common inpatient cause)
- Primary hyperparathyroidism (most common outpatient cause)
- Treatment: IV fluids, bisphosphonates, calcitonin, denosumab (refractory disease)
Sample question:
A 62-year-old woman with nephrolithiasis presents to the emergency department with muscle weakness, nausea, and confusion. ECG reveals bradycardia with a shortened QT interval. Laboratory findings include a total calcium of 14.7 mg/dL. In addition to starting intravenous isotonic saline at 200 mL/hour, which of the following is the best treatment option?
Get Free Access and Join Thousands of Happy Learners
You must be logged in to post a comment.





Comments (0)