Podcast Ep 14: Otitis Media, Hemophilia, Frostbite, & More

If opportunity doesn’t knock, build a door.
-Milton Berle
Welcome back to Episode 14! After a short break for Jeff’s honeymoon, we are back this week with more high-quality review. We have weekly episodes in the works to keep you motivated. Take note of a small change to the format this week: after each question, you will hear a one-second pause to contemplate the answer or to pause the podcast to give you even more time. We made this change in response to listener feedback; keep more feedback coming to Roshcast@roshreview.com.
We have one more exciting change to announce this week. As you go through the Rosh Review EM question bank and you come across a difficult question or a question you think would be perfect for Roshcasting, hit the “submit feedback” button and type “Roshcast.”
This will prompt the feedback to alert us, and we will work on incorporating the question as quickly as possible. Let’s get started with this week’s episode.

- The Hill-Sachs defect (a depression fracture of the posterolateral surface of the humeral head) is the most common complication of an anterior shoulder dislocation. It is seen in about 40% of cases.
- Fight bites should be treated with orally with amoxicillin-clavulanate to cover Eikenella If the patient requires IV antibiotics, ampicillin-sulbactam, cefoxitin, or piperacillin-tazobactam can be administered.
- Nursemaid’s elbow can be reduced by supination followed by flexion or by hyperpronation. X-rays are not routinely required.
Now onto this week’s podcast
Question 1
Which of the following signs has the greatest likelihood ratio for acute otitis media?
A. Impaired mobility of the tympanic membrane
B. Red tympanic membrane
C. Retracted tympanic membrane
D. Ruptured tympanic membrane
Question 2
A 4-year-old boy with hemophilia A presents to the ED after he fell from the monkey bars and struck his head on the ground. On exam, he has a large occipital hematoma and a GCS of 14. Which of the following should be administered?
A. Cryoprecipitate
B. Factor IX concentrate
C. Factor VIII concentrate
D. Recombinant human factor VIIa
Question 3
A 22-year-old woman presents with lower abdominal pain and abnormal vaginal discharge for 4 days. She is sexually active with multiple partners and does not consistently use barrier contraception. She has bilateral adnexal tenderness and yellow discharge on pelvic exam. Her urine pregnancy test is negative. In addition to a 1-time dose of ceftriaxone, what is the appropriate outpatient course of antibiotics for the patient?
A. Azithromycin 1 gram PO x 1
B. Ciprofloxacin 500 mg PO BID x 14 days
C. Doxycycline 100 mg PO BID x 14 days
D. Metronidazole 500 mg PO BID x 14 days
Question 4
A 6-year-old boy presents with a fever of 38.5°C, sore throat, and tender anterior cervical adenopathy. He does not have a cough or a runny nose. His younger sister was treated for streptococcal pharyngitis last week and his mother would like him to be treated for streptococcal infection. According to the modified Centor criteria, which of the following is the most appropriate action?
A. Empiric antibiotic treatment for streptococcal pharyngitis
B. Rapid antigen detection testing
C. Streptococcal antibody titers
D. Tonsillectomy when he recovers from this infection
Question 5
A 48-year-old homeless man is brought in by EMS. He has been walking outside in the snow for many hours wearing only tennis shoes. He is complaining that he is unable to feel his feet. On examination, his feet are cold to the touch, whitish in color, and swollen. He has delayed capillary refill and multiple clear, fluid-filled bullae on his toes. Which of the following is the most appropriate thawing technique?
A. Water immersion at temperatures between 35–36°C
B. Water immersion at temperatures between 37–39°C
C. Water immersion at temperatures between 40–42°C
D. Water immersion at temperatures between 43–45°C
Question 6
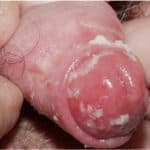
A 19-year-old man with diabetes presents with penile pain and dysuria. Physical examination of the penis reveals the image above. The patient states he has had similar episodes in the past. What management is indicated?
A. Azithromycin and ceftriaxone
B. Ciprofloxacin
C. Clotrimazole cream
D. Hydrocortisone cream

- Acute otitis media is most commonly caused viral pathogens. In cases of bacterial infection, Streptococcus, Haemophilus, and Moraxella are the three most common causes. The treatment is amoxicillin.
- In otitis media, a cloudy tympanic membrane has a likelihood ratio of 34 and impaired mobility of the tympanic membrane has a likelihood ratio of 31. A red tympanic membrane has a likelihood ratio of 2.
- Hemophilia A is caused by decreased synthesis of factor VIII. Hemophilia B or Christmas disease is caused by decreased synthesis of factor IX.
- Both hemophilia A and B are X-linked recessive diseases.
- Hemophilia A is treated with factor VIII replacement and Hemophilia B is treated with factor IX supplementation. Alternatively, cryoprecipitate can also be used in cases of shortages.
- PID is typically caused by gonorrhea or chlamydia or both. It is treated with ceftriaxone 250 mg IM once and doxycycline 100 mg PO BID x 14 days if the patient can tolerate PO. Do not confuse PID with the more benign cervicitis, which is treated with ceftriaxone and a single dose of 1 gram of azithromycin.
- Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome is a perihepatitis associated with PID. It is a difficult diagnosis to make, but suspect it in those with both pelvic and right upper quadrant pain.
- In the Modified Centor Score, you get one point for tonsillar exudates, one point for tender anterior cervical adenopathy, one point fever by history, one point for the absence of cough, and one point for age less than 15 years old. For an age over 45, you subtract one point.
- In the Modified Centor Score, for a score of 0 or 1 points, treat supportively; 2 or 3 points, test and treat if positive; and 4 or 5 points, empirically treat. The mainstay of treatment is amoxicillin.
- Frostbite should be treated with immersion in a warm water bath at 37 to 39 degrees Celsius. Water at higher temperature will warm no faster and cause increased pain and potentially tissue damage.
- Balanitis is a fungal infection of the glans typically caused by a candida infection. Treatment is with clotrimazole cream.
Hope you enjoyed this week’s episode. Keep studying and reviewing daily. We will be back next week with more high-yield review.
If you missed last week’s episode including temporal arteritis, listen here.
Until next time,
Jeff and Nachi
P.S. Check out this blog post about elite test-taking tips with Dr. Robert Hughes
Get Free Access and Join Thousands of Happy Learners
You must be logged in to post a comment.





Comments (0)