Podcast Ep 52: Temporal Arteritis, Disc Herniations, Hepatorenal Syndrome, High Pressure Injection Injury, Pediatric Rash, Hyphema

Welcome back to RoshCast for Episode 52! For those of you taking the upcoming in-training exam, an early congratulations! All of your hard work will surely pay off soon. Remember to listen to this episode and old episodes as you get closer to the end for more review. Good luck from us at the RoshCast team!
Begin to be now what you will be hereafter.
–William James
Question 1
A 64-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a right-sided headache. Past medical history includes hypertension, migraines, and polymyalgia rheumatica. Her symptoms started three days ago and have progressively worsened. She states that this headache is different from her previous migraines. It is frontal and she describes it as an ache without radiation of symptoms. She does describe worsening of symptoms with eating as well as when she brushes her hair. She admits to feeling more tired the last couple of days as well as having partial vision loss in the right eye. She denies any nausea or vomiting. Vital signs demonstrate a temperature of 38°C but otherwise are within normal limits. Physical examination is remarkable for tenderness to palpation over the right temple and visual acuities of 20/40 OS and 20/80 OD. What is the most appropriate next step in this patient’s management?
A. Intravenous methylprednisolone
B. Obtain erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein to confirm the diagnosis
C. Obtain temporal artery biopsy
D. Oral prednisone
Question 2
A 42-year-old man presents to the emergency department with lower back pain that started acutely while lifting a couch. He complains of pain radiating to the right posterolateral calf. He denies any bowel or bladder incontinence. On examination, he has decreased plantar flexion at the right ankle and numbness of the right lateral foot. Disk herniation at which level is most likely responsible for his findings?
A. L2–L3
B. L3–L4
C. L4–L5
D. L5–S1
Question 3
Which of the following is most likely to be seen in hepatorenal syndrome?
A. Arteriolar congestion
B. Histologically normal kidneys
C. Necrosis of the renal tubules
D. Segmental sclerosis of the renal glomeruli
Question 4
A 27-year-old man presents to the ED with left-hand pain. He was at work as an auto mechanic when he accidentally injected his left index finger with a grease gun. On physical exam, the digit is swollen with a central pinhole wound. The remainder of the hand exam is unremarkable. Which of the following will best determine the amount of tissue damage a substance will cause?
A. Chemical properties of the substance
B. The pressure of the injection
C. The temperature of the substance injected
D. The volume of the substance injected
Question 5
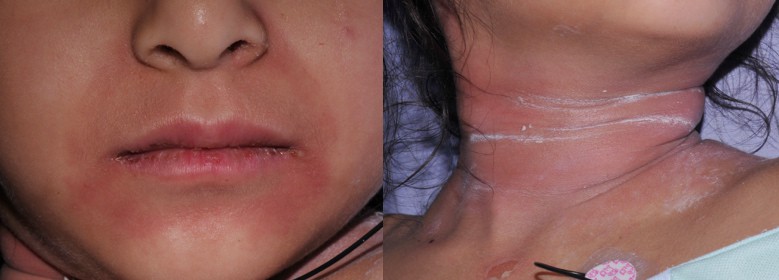
A 5-year-old girl presents to the ED with a rash that started on her face and spread to her neck, axillae, and groin. Mom states that the patient had an upper respiratory infection one week prior. On examination, the patient’s rash is tender to the touch. Which of the following statements regarding the diagnosis of this patient’s condition is correct?
A. Deep layers of the dermis are involved
B. It often leaves the patient disfigured from scarring
C. Mucous membrane involvement is common
D. The disease is caused by an exotoxin producing bacteria
Question 6
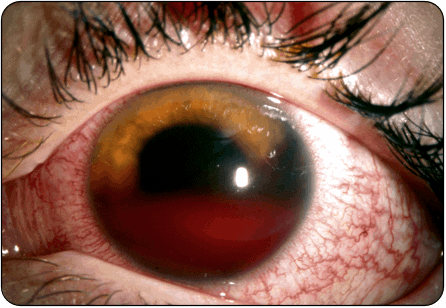
A 22-year-old man complains of pain, photophobia, and vision loss in his eye. He has a history of sickle cell anemia. His vision is 20/200 in the affected eye. Intraocular pressure is 30 mm Hg in the affected eye. You see the above finding on physical exam. Which of the following medications should be immediately administered to this patient?
A. Intravenous ketorolac
B. Intravenous mannitol
C. Topical acetazolamide
D. Topical timolol

- Vision loss is the most concerning clinical feature in patients with temporal arteritis, whereas jaw claudication is the clinical feature that is most likely associated with a positive temporal artery biopsy.
- S1 radiculopathy leads to decreased plantar flexion, numbness to the lateral foot, decreased sensation along the posterolateral calf, and decreased Achilles reflex.
- Hepatorenal syndrome leads to arteriolar constriction and the kidneys here would appear normal histologically.
- The chemical properties of the substance injected is the primary determinant of damage caused by high-pressure injection injury. While air and clean water have a benign course, paint solvents cause the most severe inflammation.
- Staph scalded skin syndrome presents in children less than 5 years old and often follows a URI. The rash starts on the face, neck, axillae, and groin, and there will be a positive Nikolsky sign.
- Patients with a spontaneous hyphema present with decreased visual acuity, elevated intraocular pressure, and an afferent pupillary defect. Immediate treatment is with agents that lower intraocular pressure including topical timolol.
That wraps up RoshCast Episode 52! Creating and producing RoshCast has been a ton of fun, but it also takes a ton of time. We are unfortunately halting production for the time being to focus on other projects. We thank you all for your long-time listenership. And don’t forget that there are 51 other episodes. Listen and re-listen on your commute to work, at the gym, or even just at a desk during dedicated study time.
A huge thanks also goes out to all of the folks at Rosh Review who have worked diligently to create high-quality clinical questions. If you need to reach us, please e-mail Nachi at nachig@gmail.com. Be sure to also check out the rest of the Rosh Review Blog for questions from prior episodes, related images, and tables, as well as bonus teaching points.
Jeff, Megha, and Nachi
Get Free Access and Join Thousands of Happy Learners
You must be logged in to post a comment.





Comments (0)